Carnivore Diet Meal Plan
Carnivore Diet Meal Plan
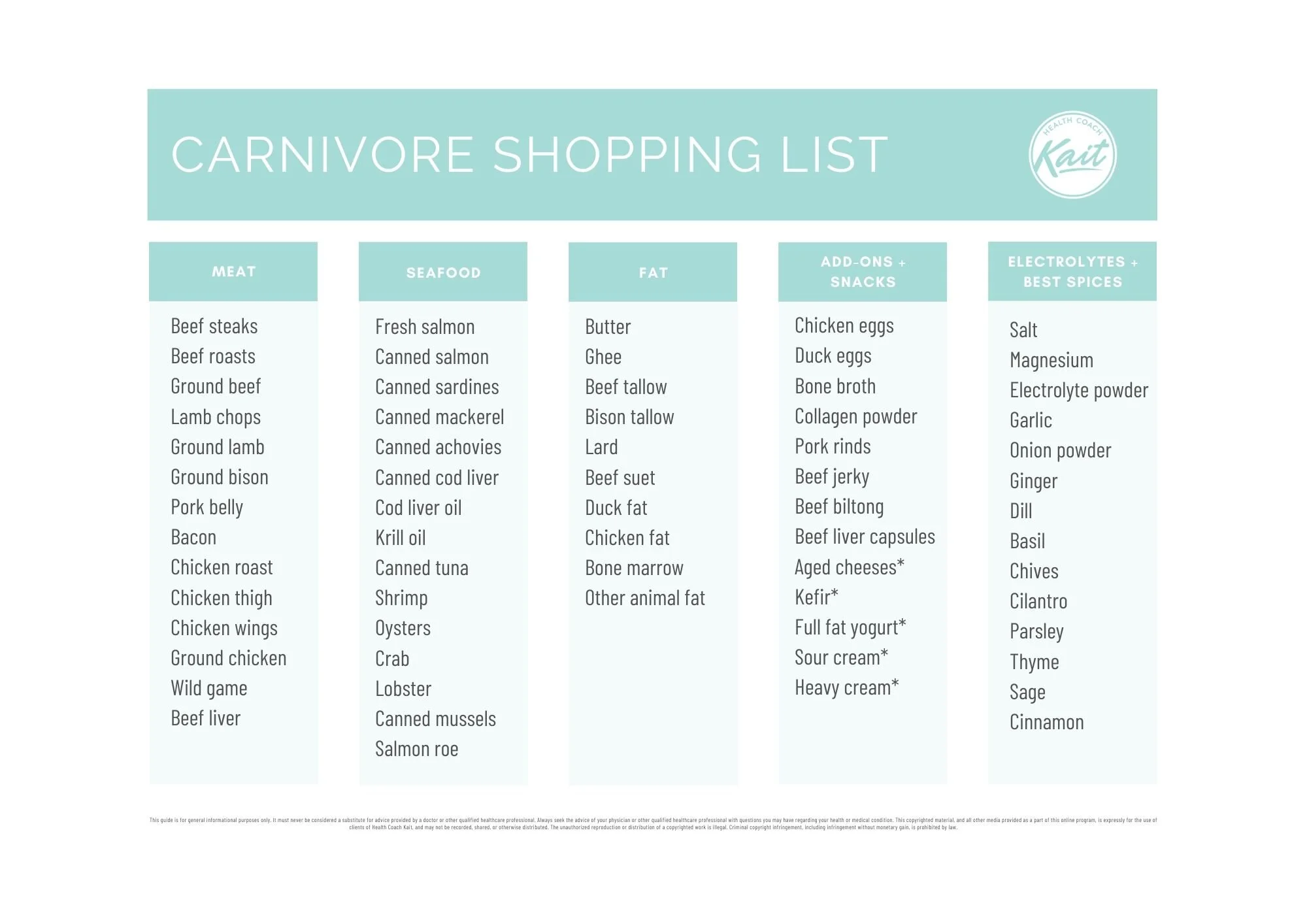
What foods can you eat on the carnivore diet? Here are the foods that are included, the foods you should avoid and what a sample day of eating looks like on the carnivore diet.
Carnivore Diet Food List
The carnivore diet includes all foods from the animal kingdom. This includes:
ruminant animal meat (beef, bison, lamb)
other animal meat (chicken, pork, turkey)
fish (salmon, sardines, mackerel)
eggs (chicken eggs, duck eggs, fish eggs)
other seafood (shrimp, oysters, lobster)
bone broth and bone marrow
animal fat (tallow, lard, duck fat)
dairy (cheese, cream, butter)
organ meats
Foods that are not apart of the carnivore diet
Any foods that are not apart of the animal kingdom are not apart of the carnivore diet. This includes:
fruits and vegetables
wheat and grains
beans and seeds
plant oils
How much to eat
The general rule when start the carnivore diet is not to track calories or macronutrients. If you are only eating animal foods, not avoiding fat and eating until satiety, you should meet your daily requirements (and not overeat) without having to track.
In order to meet your protein needs, you want to be eating around 1g of protein per pound of your goal bodyeweight. If your goal bodyweight is 140lb, eat 140g of protein. Fat can be added to this until you reach satiety.
Sample day of eating
Here is an example of what a sample day of eating might look like on the carnivore diet.
Morning
Black coffee
Meal 1
5 eggs cooked in butter
2 rashers of bacon
Meal 2
Steak (or other cut of meat) cooked in animal fat
Side of shrimp
It really is that simple! Personally, I usually eat two meals a day and find that works best for me. But some people eat three and some people eat one - there is no right or wrong way to do it!
Download Your Carnivore Diet Shopping List Now!
Take the guesswork out of meal planning and ensure you’re fueling your body with the best carnivore-friendly foods.
This website is for general informational purposes only. It must never be considered a substitute for advice provided by a doctor or other qualified healthcare professional. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified healthcare professional with questions you may have regarding your medical condition.